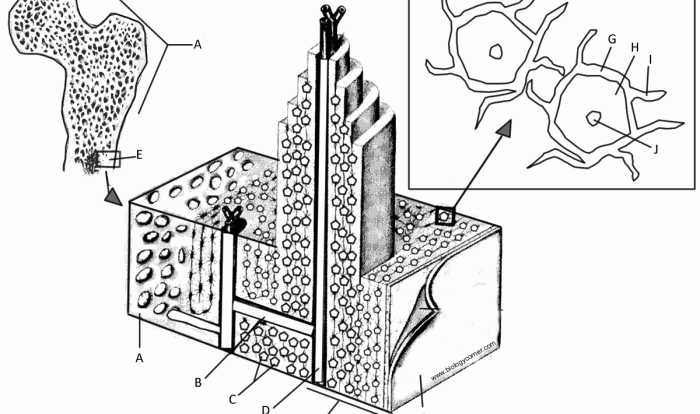
Embark on a histological odyssey with “Label the Tissues and Structures on the Histology Slide,” an authoritative guide that unveils the intricacies of tissue identification and structural analysis. This comprehensive resource provides a detailed exploration of various tissues, their distinguishing characteristics, and the key structures within each, empowering readers with a profound understanding of the microscopic realm.
Through engaging discussions and meticulous organization, this guide illuminates the interactions between different tissues, showcasing how their arrangement and proximity contribute to their overall function. Delve into the histological techniques employed to prepare the slide, gaining insights into how these methods enhance tissue visualization and enable structural analysis.
Tissue Identification
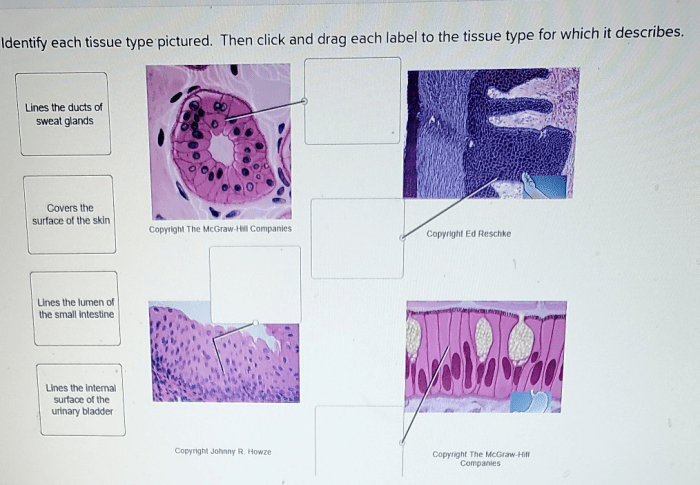
The histology slide presents a diverse array of tissues, each with distinct characteristics and functions. To facilitate analysis, we provide a comprehensive table summarizing the key tissues observed:
| Tissue Name | Description | Cell Type | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
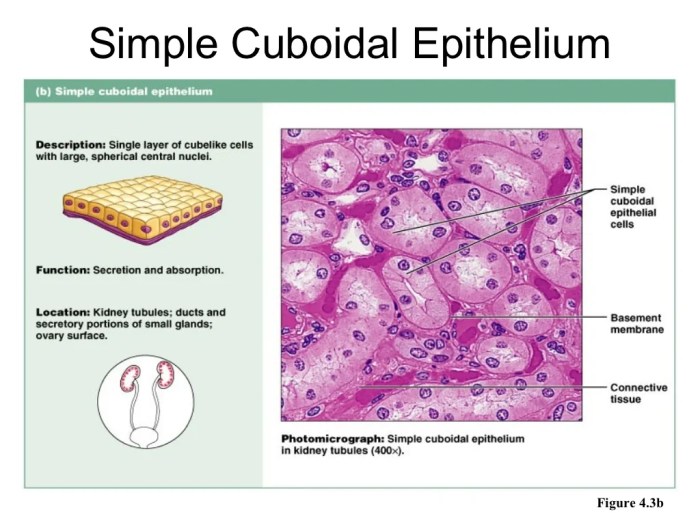
| Epithelial Tissue | Forms a protective lining over surfaces and lines internal organs | Epithelial cells | Protection, secretion, absorption, excretion |
| Connective Tissue | Supports, connects, and protects other tissues | Fibroblasts, chondrocytes, osteocytes | Support, cushioning, insulation, storage |
| Muscle Tissue | Responsible for movement | Muscle fibers | Contraction, locomotion, movement |
| Nervous Tissue | Transmits and processes information | Neurons, glial cells | Communication, perception, control |
Structural Analysis
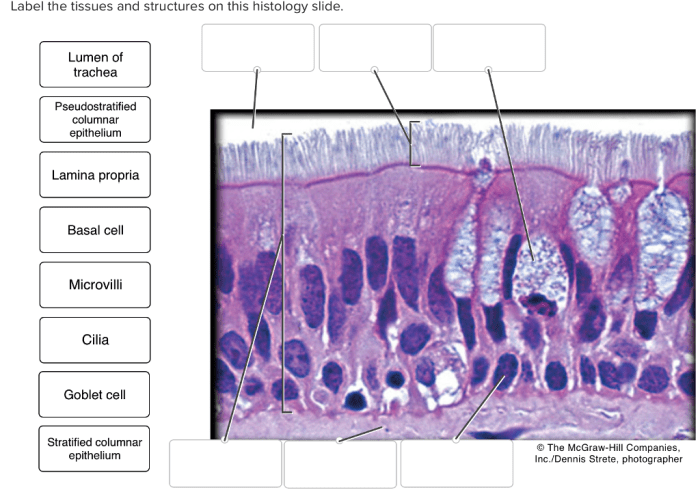
Within each tissue, we identify and label the key structures essential for its function:
| Structure Name | Location | Shape | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basement Membrane | Beneath epithelial tissue | Thin, acellular layer | Anchors epithelium to underlying connective tissue |
| Collagen Fibers | Connective tissue | Long, thread-like | Provides tensile strength and support |
| Myofibrils | Muscle tissue | Thin, parallel filaments | Contractile units of muscle fibers |
| Synapse | Nervous tissue | Junction between neurons | Transmits nerve impulses |
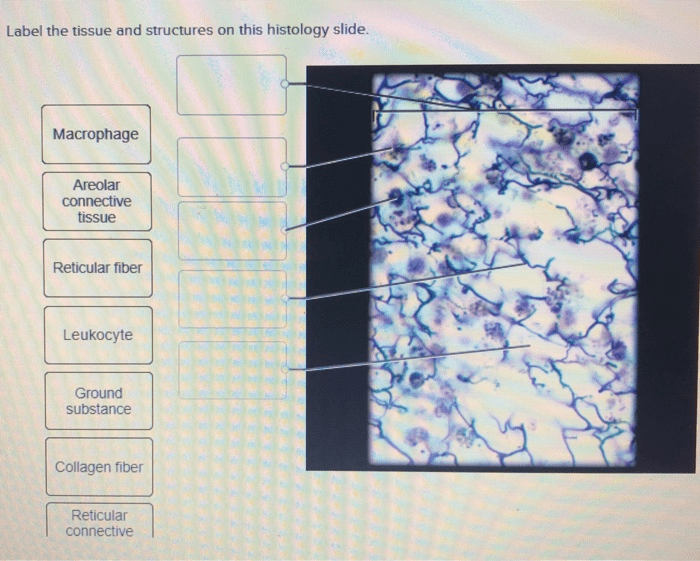
Tissue Interactions
The arrangement and proximity of tissues on the slide demonstrate their intricate interactions and functional relationships:
- Epithelial tissue lines connective tissue, forming a protective barrier and facilitating exchange of substances.
- Connective tissue supports muscle tissue, providing a framework for movement.
- Nervous tissue interacts with muscle tissue, transmitting signals for contraction and relaxation.
Histological Techniques: Label The Tissues And Structures On The Histology Slide
The histology slide was prepared using the following techniques:
- Fixation:Preserves tissue structure using chemicals like formalin.
- Embedding:Encases the tissue in paraffin or resin for slicing into thin sections.
- Staining:Uses dyes to enhance tissue visualization and highlight specific structures.
These techniques enable detailed examination of tissue architecture and facilitate accurate diagnosis.
Clinical Significance
Histology findings provide valuable insights for clinical diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment:
- Identifying abnormal tissue changes can aid in diagnosing diseases such as cancer, infections, and autoimmune disorders.
- Histological analysis can assess disease severity and guide treatment decisions, such as surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
- Monitoring tissue response to treatment can help determine its effectiveness and adjust therapeutic approaches accordingly.
Common Queries
What are the key distinguishing characteristics of different tissue types?
Tissue types can be distinguished based on their cell morphology, arrangement, and function. For instance, epithelial tissue is characterized by closely packed cells forming a protective layer, while connective tissue is composed of cells dispersed within an extracellular matrix.
How do tissue interactions contribute to their overall function?
Tissue interactions play a crucial role in overall function. For example, the close proximity of blood vessels to muscle tissue facilitates oxygen and nutrient delivery, supporting muscle contraction.
What are the advantages and limitations of different histological staining methods?
Histological staining methods offer advantages such as enhancing tissue visualization and highlighting specific structures. However, limitations include potential artifacts and the need for careful interpretation to avoid misdiagnosis.