POGIL DNA structure and replication provide a captivating framework for comprehending the intricate nature of DNA. This discourse delves into the molecular composition and structural intricacies of DNA, unraveling the fundamental principles governing its replication. Through engaging POGIL activities, learners embark on an interactive journey, simulating the processes involved in DNA replication and fostering a deeper understanding of this critical biological mechanism.
The subsequent paragraphs delve into the diverse applications of DNA analysis, ranging from forensic investigations to medical diagnostics. Ethical considerations surrounding the use of DNA information are also explored, emphasizing the importance of responsible and informed decision-making in this rapidly evolving field.
DNA Structure
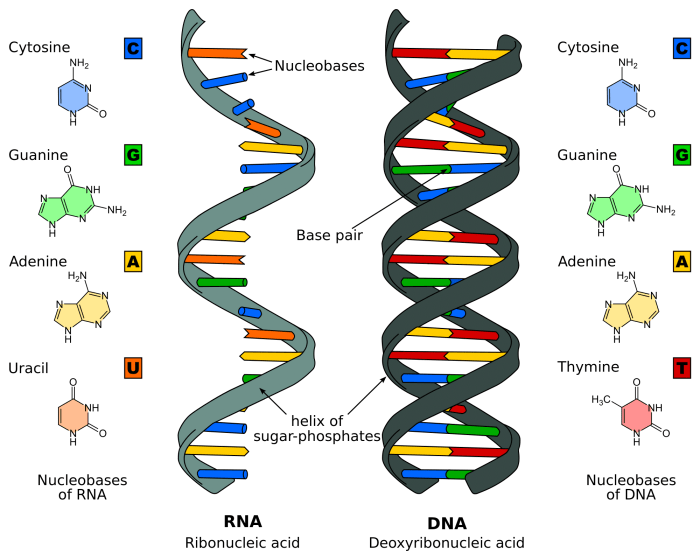
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is found in the nucleus of cells and is made up of two long chains of nucleotides twisted together to form a double helix.
Chemical Composition of DNA
Each nucleotide in DNA consists of three parts: a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up with each other in a specific way: A always pairs with T, and C always pairs with G.
This pairing is known as complementary base pairing.
Structure of the DNA Molecule
The double helix structure of DNA was first proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953. The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between the complementary base pairs. The double helix is twisted into a spiral shape, with the nitrogenous bases facing inward and the deoxyribose sugar-phosphate backbone facing outward.
The DNA molecule is very long. In humans, for example, the DNA in each cell is about 2 meters long. To fit inside the cell, the DNA is packaged into structures called chromosomes. Chromosomes are made up of DNA wrapped around proteins called histones.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which a cell duplicates its DNA. It is a fundamental process in cell division and ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material.
DNA replication is carried out by a complex of enzymes, including DNA polymerase, helicase, and ligase. DNA polymerase is the enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands, helicase unwinds the DNA double helix, and ligase joins the new DNA strands together.
Role of Enzymes in DNA Replication
- DNA polymerase: Synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the 3′ end of a growing DNA strand.
- Helicase: Unwinds the DNA double helix by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases.
- Ligase: Joins the new DNA strands together by forming phosphodiester bonds between the nucleotides.
Importance of DNA Replication for Cell Division
DNA replication is essential for cell division because it ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the genetic material. This is important for the following reasons:
- Growth and development: DNA replication is necessary for the growth and development of an organism.
- Repair: DNA replication can repair damaged DNA, which is essential for maintaining the integrity of the genome.
- Reproduction: DNA replication is essential for reproduction, as it allows the genetic material to be passed on from one generation to the next.
POGIL Activities: Pogil Dna Structure And Replication
POGIL (Process Oriented Guided Inquiry Learning) activities are designed to engage students in active learning by having them work in small groups to explore and understand scientific concepts.
POGIL activities can be used to teach a variety of DNA concepts, including DNA structure, DNA replication, and gene expression. These activities are particularly effective for helping students to develop a deeper understanding of the molecular basis of life.
Design a POGIL activity that helps students understand DNA structure
One way to design a POGIL activity on DNA structure is to have students build models of DNA molecules using materials such as pipe cleaners, beads, and straws. Students can then use these models to investigate the different components of DNA and how they interact with each other.
For example, students can use their models to determine the following:
- The relative sizes of the different DNA components (e.g., nucleotides, bases, deoxyribose sugars, phosphate groups)
- The shape of the DNA molecule (e.g., double helix)
- The types of bonds that hold the DNA molecule together (e.g., covalent bonds, hydrogen bonds)
Create a POGIL activity that allows students to simulate DNA replication
Another way to design a POGIL activity on DNA replication is to have students simulate the process of DNA replication using materials such as paper, scissors, and tape.
In this activity, students can act as the different enzymes involved in DNA replication, such as DNA polymerase and helicase. Students can then follow the steps of DNA replication to create a new strand of DNA.
For example, students can use their models to simulate the following steps of DNA replication:
- Unwinding the DNA molecule
- Separating the two strands of DNA
- Synthesizing new strands of DNA
- Joining the new strands of DNA together
Discuss the benefits of using POGIL activities to teach DNA concepts
There are many benefits to using POGIL activities to teach DNA concepts. These benefits include:
- POGIL activities help students to develop a deeper understanding of the molecular basis of life.
- POGIL activities are hands-on and engaging, which helps to keep students interested in the material.
- POGIL activities promote collaboration and teamwork among students.
- POGIL activities can be used to assess student learning in a variety of ways.
Applications of DNA Analysis
DNA analysis has revolutionized various fields, including forensics, medicine, and ethics.
Forensic Applications, Pogil dna structure and replication
In forensics, DNA analysis plays a crucial role in:
- Identifying individuals from crime scene evidence, such as blood, hair, or saliva.
- Linking suspects to victims or crime scenes through DNA profiling.
- Exonerating wrongfully convicted individuals by comparing DNA evidence to crime scene samples.
Medical Applications
DNA analysis has significant applications in medical diagnosis:
- Diagnosing genetic disorders by identifying mutations or variations in DNA sequences.
- Determining predisposition to diseases, such as cancer or heart disease, based on genetic markers.
- Developing personalized treatments tailored to an individual’s genetic profile.
Ethical Implications
The widespread use of DNA analysis raises ethical concerns:
- Privacy concerns, as DNA information can reveal personal and sensitive data.
- Potential for discrimination based on genetic predispositions or characteristics.
- Questions about the ownership and control of genetic information.
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of DNA replication?
DNA replication is essential for cell division, ensuring the accurate transmission of genetic information to daughter cells.
How do POGIL activities enhance DNA learning?
POGIL activities provide an interactive and collaborative environment, promoting active learning and deeper comprehension of DNA concepts.
What are the ethical considerations in DNA analysis?
Ethical considerations include privacy concerns, potential discrimination, and the responsible use of genetic information.