Welcome to the bone matrix coloring answer key, where the mysteries of bone health unravel. Dive into a captivating journey as we unveil the purpose, techniques, and applications of this essential histological tool. Prepare to witness the secrets of your skeletal system laid bare!
Bone matrix coloring, a cornerstone of histology, empowers us to visualize and decipher the intricate details of our bones. Through various staining methods, we can uncover abnormalities, assess bone quality, and unravel the underlying causes of bone diseases.
Bone Matrix Coloring Overview
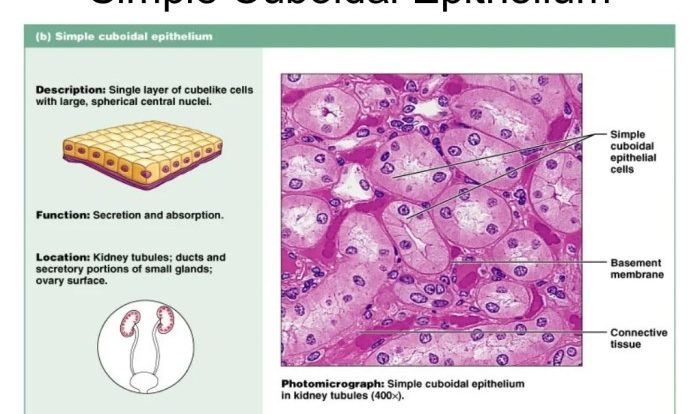
Bone matrix coloring is a histological technique used to differentiate between different types of bone tissue. It involves staining the bone matrix with dyes or stains that selectively bind to specific components of the bone, such as collagen, calcium, or phosphate.
This allows researchers to visualize and study the structure and composition of bone tissue under a microscope.There are several different types of bone matrix coloring techniques, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Some of the most common techniques include:
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining
H&E staining is a basic histological staining technique that uses hematoxylin to stain nuclei blue and eosin to stain cytoplasm and extracellular matrix pink. It is a simple and inexpensive technique that provides good general visualization of bone tissue. However, it does not provide much information about the specific composition of the bone matrix.
Von Kossa Staining
Von Kossa staining is a specific histological staining technique that uses silver nitrate to stain calcium deposits black. It is used to visualize the distribution of calcium in bone tissue and can be helpful in diagnosing conditions such as osteoporosis.
However, it can be difficult to interpret the results of Von Kossa staining, as it can also stain other types of calcium deposits, such as those found in calcified cartilage.
Alizarin Red Staining
Alizarin red staining is a specific histological staining technique that uses alizarin red to stain calcium deposits red. It is used to visualize the distribution of calcium in bone tissue and can be helpful in diagnosing conditions such as osteoporosis.
Alizarin red staining is more specific than Von Kossa staining and is easier to interpret.
Trichrome Staining
Trichrome staining is a histological staining technique that uses three different dyes to stain different components of the bone matrix. It is used to visualize the distribution of collagen, calcium, and phosphate in bone tissue. Trichrome staining can provide more information about the composition of the bone matrix than H&E staining, but it is more complex and time-consuming to perform.
Feeling a bit rusty on your bone matrix coloring knowledge? Sharpen your skills with our comprehensive vet science CDE practice test . It’s packed with challenging questions to help you master this crucial topic and prepare for the big day.
Once you’ve conquered the practice test, come back and check out our bone matrix coloring answer key for a thorough review.
Bone Matrix Coloring Methods: Bone Matrix Coloring Answer Key

Bone matrix coloring is a technique used to visualize and differentiate the various components of bone tissue under a microscope. There are several staining methods available, each employing specific reagents to highlight different structural features of the bone matrix.
Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Stain
H&E staining is a widely used technique for general tissue examination, including bone tissue. It utilizes two dyes, hematoxylin and eosin, to stain different cellular components and extracellular matrix elements.
- Hematoxylin:A basic dye that stains acidic components, such as cell nuclei, blue or purple.
- Eosin:An acidic dye that stains basic components, such as cytoplasm and extracellular matrix, pink or red.
The H&E staining procedure involves the following steps:
- Deparaffinization and rehydration of the tissue section
- Staining with hematoxylin
- Differentiation with acid alcohol
- Bluing with ammonia water
- Staining with eosin
- Dehydration and clearing of the tissue section
- Mounting the section on a slide
Alternative Staining Methods
In addition to H&E staining, there are other staining methods that can be used to visualize specific components of bone matrix.
- Masson’s Trichrome Stain:This stain differentiates between collagen fibers (blue), muscle fibers (red), and nuclei (black).
- von Kossa Stain:This stain highlights calcium deposits in bone tissue by forming a black precipitate.
Bone Matrix Coloring Interpretation
Bone matrix coloring is a valuable technique that can provide valuable information about the health and condition of bone tissue. By staining the bone matrix with different dyes, pathologists can identify a variety of abnormalities that may not be visible under normal microscopy.
The normal appearance of bone matrix under a microscope is a uniform, pale pink color. The matrix should be smooth and evenly distributed, with no visible cracks or defects. However, in certain pathological conditions, the bone matrix may exhibit abnormalities in color, texture, or distribution.
Types of Bone Matrix Abnormalities
Some of the most common types of bone matrix abnormalities that can be detected using bone matrix coloring include:
- Osteomalacia:This condition is characterized by a softening of the bone matrix due to a deficiency of vitamin D or calcium. The bone matrix appears pale and translucent, with a lack of mineralization.
- Osteoporosis:This condition is characterized by a decrease in bone density and an increase in bone porosity. The bone matrix appears thin and fragile, with a loss of trabecular structure.
- Paget’s disease of bone:This condition is characterized by an abnormal remodeling of bone tissue. The bone matrix appears thickened and irregular, with areas of increased and decreased mineralization.
- Fibrous dysplasia:This condition is characterized by the replacement of bone tissue with fibrous tissue. The bone matrix appears pale and fibrous, with a lack of mineralization.
- Osteosarcoma:This is a malignant tumor of bone that can produce a variety of bone matrix abnormalities. The bone matrix may appear disorganized and chaotic, with areas of increased and decreased mineralization.
Interpretation of Results
The interpretation of bone matrix coloring results must be done in the context of a patient’s medical history and clinical presentation. For example, a patient with a history of vitamin D deficiency may be more likely to have osteomalacia, while a patient with a history of osteoporosis may be more likely to have a decrease in bone density.
By combining the results of bone matrix coloring with other clinical information, pathologists can make an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Applications of Bone Matrix Coloring
Bone matrix coloring is a valuable tool in various fields, including medicine, research, and forensic investigations.
Diagnosis of Bone Diseases
Bone matrix coloring aids in the diagnosis of bone diseases such as osteoporosis and osteomalacia. In osteoporosis, reduced bone mineralization leads to decreased staining intensity, while in osteomalacia, abnormal mineralization patterns can be observed.
Assessment of Bone Quality
In research settings, bone matrix coloring is used to assess bone quality. It can reveal information about bone density, mineralization distribution, and microarchitecture, providing insights into bone health and disease progression.
Forensic Investigations, Bone matrix coloring answer key
Bone matrix coloring plays a role in forensic investigations. It can help determine the age of skeletal remains, identify individuals, and assess trauma or disease history.
Troubleshooting Bone Matrix Coloring
Bone matrix coloring techniques can encounter various problems that affect the accuracy and reliability of the results. Understanding these common issues and implementing appropriate troubleshooting measures is crucial to avoid artifacts and ensure the validity of the analysis.
Below are some common problems and troubleshooting tips for bone matrix coloring:
Uneven Staining
- Problem:Uneven staining, resulting in patchy or inconsistent coloring.
- Troubleshooting Tip:Ensure thorough mixing of the staining solutions and adequate immersion time for the bone specimens. Consider using a gentle agitation or vacuum infiltration technique to promote uniform penetration of the stains.
Non-Specific Staining
- Problem:Non-specific staining, where areas of the bone matrix that should not be stained are colored.
- Troubleshooting Tip:Optimize the staining protocol by adjusting the concentration of the staining solutions and the incubation time. Use appropriate blocking agents or counterstains to minimize non-specific binding of the stains.
Artifacts
- Problem:Artifacts, such as bubbles or precipitates, appearing in the stained bone sections.
- Troubleshooting Tip:Carefully prepare the staining solutions and filter them before use. Ensure proper dehydration and clearing steps during the tissue processing to remove air bubbles and other artifacts.
Fading or Loss of Stain
- Problem:Fading or loss of stain over time, compromising the visibility and interpretation of the results.
- Troubleshooting Tip:Use high-quality stains and appropriate mounting media to minimize fading. Consider using UV-resistant coverslips or storing the stained sections in a dark and cool environment to prevent photobleaching.
FAQ
What is the purpose of bone matrix coloring?
Bone matrix coloring allows us to visualize and examine the structure and composition of bone tissue, aiding in the diagnosis of various bone diseases.
What is the most common bone matrix coloring technique?
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is the most widely used bone matrix coloring technique, providing a clear distinction between different bone components.
How can bone matrix coloring help diagnose bone diseases?
By examining the color and distribution of stained bone tissue, pathologists can identify abnormalities indicative of specific bone diseases, such as osteoporosis and osteomalacia.